In the realm of design, there are various disciplines that cater to different aspects of creating a product or a solution. Among these, Product Design and UX/UI Design are two significant fields that often overlap and yet have distinct characteristics. This blog post aims to elucidate the differences and similarities between these two design disciplines, particularly in the context of product design companies in India.
Understanding Product Design
Product Design is a comprehensive term that refers to the entire process of creating and developing a new product to be sold by a business or enterprise to its customers. It not only involves the design aesthetics but also the product’s usability, functionality, and overall value.
In the context of product design companies in India, product design has evolved significantly over the years. With the rise of digital technology and user-centered design, product designers are now more focused on creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. They are not just creating aesthetically pleasing objects, but they are also concerned with the usability and the overall experience a product offers.
The Scope of Product Design
Product design is a broad field that encompasses various aspects of a product:
Functionality: The product should perform its intended function effectively and efficiently. This involves defining the problem the product will solve and how it will solve it.
Usability: The product should be easy to use. This involves designing the product in such a way that users can intuitively understand how to use it.
Aesthetics: The product should be visually appealing. This involves choosing colors, shapes, textures, and other visual elements that make the product attractive.
Ergonomics: The product should be comfortable to use. This involves designing the product to fit the user physically, ensuring that it is not straining or uncomfortable to use.
Manufacturability: The product should be able to be manufactured efficiently and at a reasonable cost. This involves designing the product in such a way that it is easy to produce and assemble.
Sustainability: The product should be environmentally friendly. This involves choosing materials and manufacturing processes that minimize the product’s environmental impact.
The Role of a Product Designer
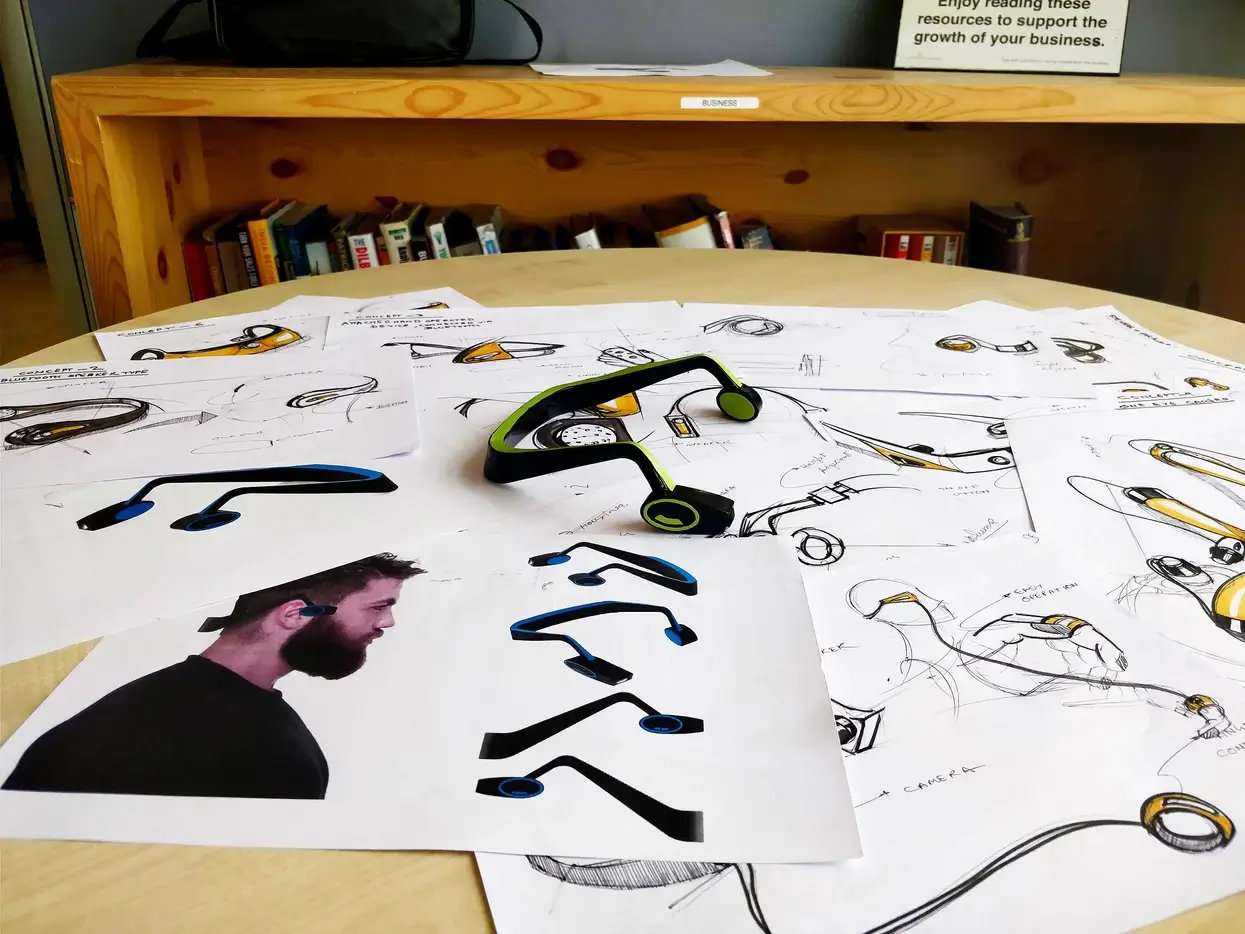

A product designer plays a crucial role in the product design process. They are responsible for the entire product design process, from identifying user needs and generating ideas to creating prototypes and finalizing the design. They need to have a deep understanding of the users and their needs, a good sense of aesthetics, a solid knowledge of materials and manufacturing processes, and an ability to solve problems creatively.
Strategies for Concept Generation
Concept generation is a creative process that involves coming up with a wide range of ideas for new products. It is a crucial step in the product design process as it sets the foundation for the subsequent stages of design and development. Here are some commonly used strategies for concept generation:
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a widely used technique for generating a large number of ideas. It involves a group of people, usually a team of designers, who come together to generate ideas around a specific problem or topic. The key to effective brainstorming is to encourage free thinking and discourage criticism of ideas during the session. All ideas, no matter how outlandish, are welcomed.
Sketching
Prototyping
Prototyping involves creating a preliminary model of the product. It allows designers to test their ideas, identify potential issues, and refine their concepts based on feedback. Prototypes can range from simple paper models to interactive digital models. The key is to create a tangible representation of the concept that can be tested and evaluated.
User Co-Creation
User co-creation involves collaborating with users to generate concepts. This approach ensures that the concepts developed align with user needs and expectations. It also allows designers to gain valuable insights from users, who are often the best source of information about what works and what doesn’t in a product.
The Role of Product Design Studios in Concept Generation
Product design studios in Bangalore and other parts of India play a pivotal role in concept generation. These studios are often home to a diverse team of designers, engineers, and researchers who bring a wealth of expertise and creativity to the table.
Collaborative Environment
Product design studios often foster a collaborative environment where team members can freely share ideas and feedback. This collaborative culture is crucial for concept generation as it encourages the free flow of ideas and promotes creative problem-solving.
User-Centric Approach
Many product design studios adopt a user-centric approach to design. They invest time and resources in understanding the user’s needs, behaviors, and context of use. This deep understanding of the user informs the concept generation process, ensuring that the concepts developed are relevant and valuable to the user.
Leveraging Technology
Product design studios also leverage technology in the concept generation process. They use a variety of tools and technologies, from sketching and 3D modeling software to virtual reality, to visualize and test their concepts. These tools enable designers to explore different design possibilities and refine their concepts based on feedback and testing.
Industry Knowledge
Product design studios bring a deep understanding of the industry and market trends. This knowledge informs the concept generation process, helping designers to create concepts that are not only innovative but also viable in the market.
The Journey from Industrial Design Development to Product Manufacturing
Once the industrial design has been developed, the next step is product manufacturing. This involves translating the design specifications into a physical product. It’s important to understand that while industrial design development is about creating the design, product manufacturing is about turning that design into a tangible product that can be manufactured and sold.
Translating Design Specifications into a Physical Product
The process of translating design specifications into a physical product involves several steps. First, the design specifications need to be reviewed and finalized. This includes the product’s dimensions, materials, colors, and other details.
Next, a prototype of the product is often created. This allows the design team to see how the product will look and function in real life. It also provides an opportunity to test the product and make any necessary adjustments before mass production begins.
Selecting a Manufacturer
Once the design specifications have been finalized and a prototype has been created and tested, the next step is to select a manufacturer. This involves researching potential manufacturers, requesting quotes, and evaluating each manufacturer’s capabilities, quality standards, and pricing.
Overseeing the Manufacturing Process
After a manufacturer has been selected, the design team will need to oversee the manufacturing process. This involves monitoring the production schedule, inspecting the quality of the products, and addressing any issues that arise. Regular communication with the manufacturer is key to ensuring a smooth production process.
Quality Control and Testing
Quality control and testing are crucial steps in the product manufacturing process. This involves inspecting the products to ensure they meet the design specifications and quality standards. It also involves testing the products to ensure they function as intended.
Understanding UX/UI Design
UX/UI Design is a discipline within the design field that focuses on both the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) aspects of a product, with UX encompassing a broader range of considerations beyond just the interface. The goal of UX Design is to meet user needs and goals effectively and efficiently, ensuring that users can accomplish tasks with ease and satisfaction.
User Experience (UX) Design
User Experience Design, often abbreviated as UX Design, is the process of enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the user and the product. UX Design involves research to understand the user’s needs and behaviors, creating user personas, mapping user journeys, and designing the overall experience a user has with a product.
User Interface (UI) Design
User Interface Design, or UI Design, on the other hand, is the process of making interfaces in software or computerized devices with a focus on looks or style. It is about designing the visual elements that the user interacts with, including buttons, icons, spacing, and responsive design. The goal of UI Design is to visually guide the user through a product’s interface and make the interaction as simple and efficient as possible.
The Intersection of Product Design and UX/UI Design
While Product Design and UX/UI Design are distinct disciplines, they often overlap in the design process. Product designers need to consider the user experience and interface when designing a product, and UX/UI designers often need to consider the physical aspects of a product. In many product design studios in Bangalore and other parts of India, you’ll find product designers and UX/UI designers working closely together to create products that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also provide a great user experience.
Conclusion
Industrial design development and product manufacturing are critical phases in the product design process. They involve translating innovative concepts into tangible products that meet user needs and are feasible to manufacture and sell.
The journey from concept generation to product manufacturing is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of user needs, creativity, technical knowledge, and a keen eye for detail. However, with the right strategies and resources, it’s a journey that any business owner can undertake successfully.
By understanding the nuances of industrial design development and product manufacturing, business owners can navigate the product design process more effectively. They can leverage the expertise of product design studios in Bangalore and other parts of India to create innovative products that not only meet user needs but also provide a competitive edge in the market.
Remember, the journey of product design is as important as the destination. It’s about learning, iterating, and continuously improving – to create products that truly meet user needs and drive business success.
This blog post is intended for everyone interested in understanding the differences and similarities between Product Design and UX/UI Design. It provides a comprehensive overview of the topic and offers insights into the Indian design industry.
Please note that the views and opinions expressed in this blog post are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any industrial design studios in Bangalore or elsewhere

Abhishek Reddy Gujjala
Criador Labs is an innovative product design studio that is future-focused and renowned for turning bold ideas into exquisitely engineered products. With expertise in Medical Devices, Consumer Technology, and Industrial IoT (Internet of Things), we combine strategy, design, and usability to deliver tangible creative solutions. Founded by Abhishek Reddy Gujjala, an entrepreneur passionate about purposeful innovation, Criador Labs reflects his vision of creating meaningful products that solve real-world problems through thoughtful design.

